Business Brief
Real-World Evidence: Using Systematic Literature Reviews for Evidence Synthesis and Study Design Planning for Pharmaceuticals, Medical Devices, and DiagnosticsA guide for RWE researchers using systematic literature reviews
Real-world evidence (RWE) includes data from retrospective or prospective studies and provides insights beyond the context of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). RWE studies assess both treatment approaches and health outcomes of patients in typical clinical practice and are increasingly used to support regulatory interactions and product commercialization. RWE is essential for establishing a product’s value proposition from the perspective of a payer or health technology assessment agency.
RWE has shown immense value for companies that have invested the resources to develop, measure, and apply it meaningfully. C-suite and bedside clinicians alike increasingly view RWE as strategically important in healthcare decision making. It is not unusual for an organization to implement multiple, if not dozens of RWE studies simultaneously at different stages. This high study volume means that evidence packages are constantly expanding, and it is important that organizations stay on top of their research findings as well as those of competitors.
Growth of RWE in Drug Development
94% of the companies surveyed in Deloitte’s 2020 RWE Benchmarking Study2 believe RWE in R&D will become important or very important to their organization by 2022.
Almost all of these companies expect to increase investments in technology, talent, and external partnerships to strengthen their RWE capabilities.
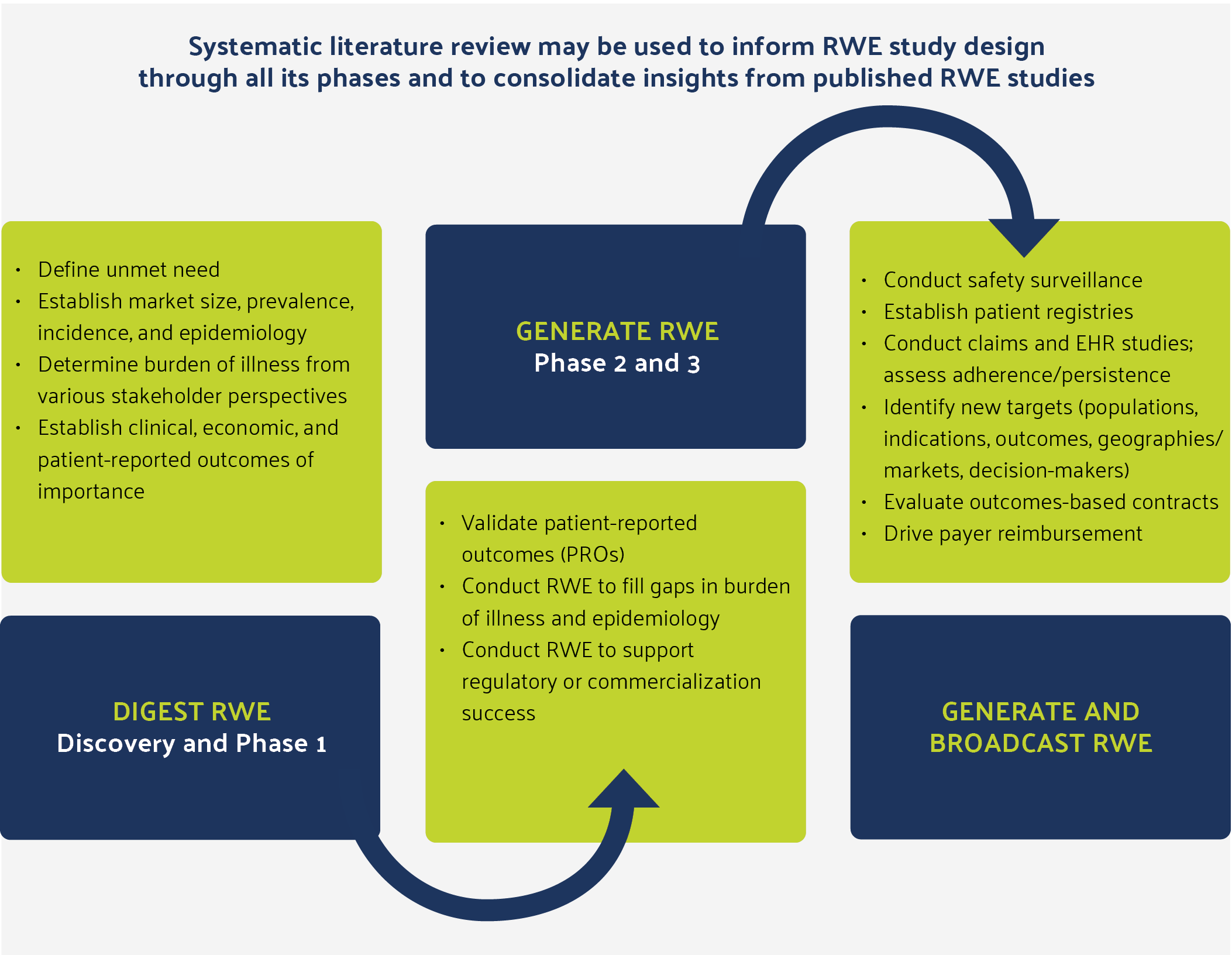
Figure 1: Real-World Evidence Is Important at Every Phase of Drug, Medical Device, and Diagnostic Development
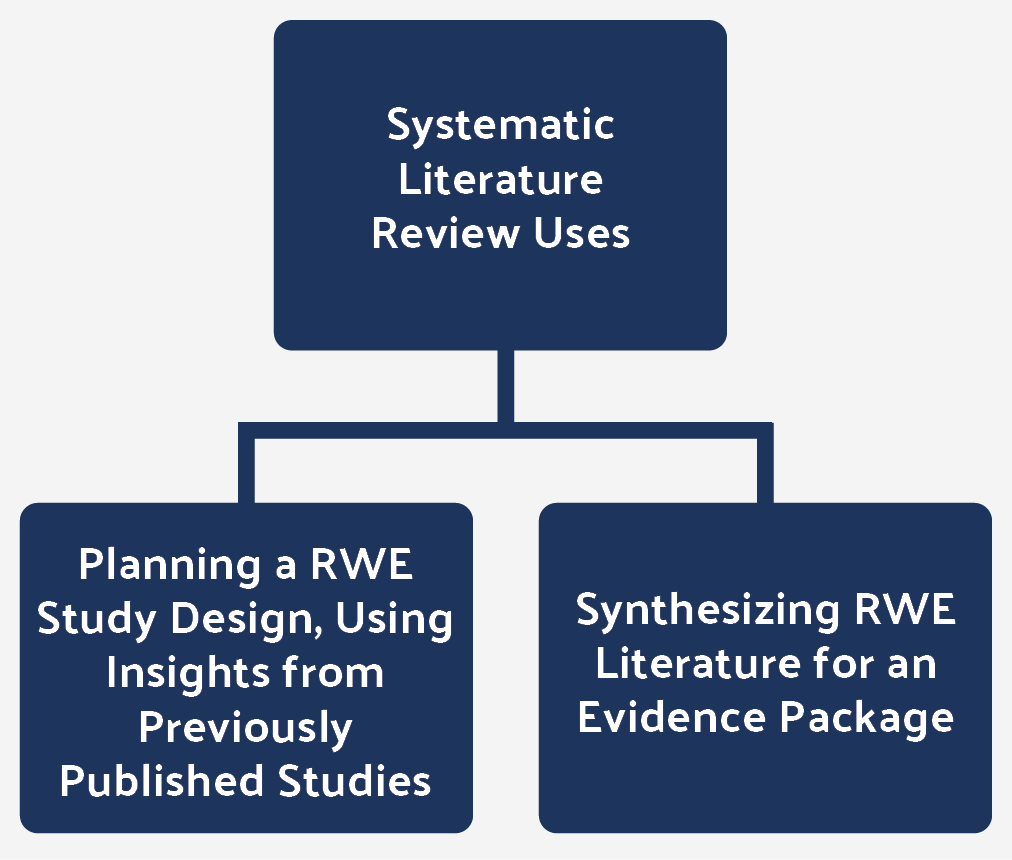
Figure 2: Systematic literature reviews are often used in two ways for RWE.
It is also common to present a consolidated evidence package of research, both for clinical trials and RWE studies, when seeking to attain market access with a payer or a health technology assessment agency. Again, systematic literature reviews may be used.
Evidence synthesis is the process of retrieving, evaluating, combining, and summarizing the findings of all relevant insights on a certain subject area. The purpose is to identify the drivers of effectiveness and safety (epidemiologic, clinical, economic, and/or patient-reported) based on the population or healthcare system characteristics that may interact with the therapeutic entity under study.
A high-quality systematic literature review is designed in response to a clearly articulated question. It uses explicit, systematic, and reproducible methods to identify, select, critically appraise, qualitatively analyze, and interpret all relevant evidence. SLRs often require periodic updates to include new evidence, methods, or analyses, or they may be “living” systematic reviews, which are continually updated.

According to Deloitte’s 2020 RWE Benchmarking Study, one of the primary organizational goals of the surveyed companies is to use more robust centralized cloud-based platforms with comprehensive capabilities, including knowledge management and self-service analytics applications. This is not limited to primary data. A robust systematic literature review platform for literature management is an essential part of a high-quality evidence ecosystem.
Examples of Systematic Literature Reviews of Real World Evidence, using DistillerSR
- CDK4/6 inhibitors in HR+/HER2- advanced/ metastatic breast cancer: a systematic literature review of real-world evidence studies5
- Systematic literature review of the epidemiology and clinical burden of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis6
- Cost analyses of prosthetic devices: a systematic review7
- Enables easy and efficient management of even broad and complex literature-retrieval, faster
- Reduces screening time
- Minimizes redundant data through fast, reliable deduplication
- Eliminates need for end-of-review search update
- Lowers costs and time to identify relevant evidence
- Monitors, manages and tracks all references, meta-data, and full text procurement
- Tracks every reference, every change, and every cell of data to ensure your review is audit-ready
- Meets highest standards for reproducibility
- Improves visibility into reviewer decisions
- Reduces and identifies errors
- Improves regulatory viability of evidence synthesis
- Works the way you prefer with 100% configurable workflows
- Provides standard, repeatable processes for your entire organization
- Optimizes team collaboration by using cloud-based standardized processes regardless of location
- Tracks review and team progress in real time
- Enhances staff and workflow efficiencies
DistillerSR by the Numbers
Cut down review time between 35% and 50%. Find 95% of relevant records 60% sooner.
Leverage DistillerSR to automate, manage and perform literature reviews for RWE studies. Learn more here.
- Meticulous Research. Real-world evidence (RWE) solutions market: Global opportunity analysis and industry forecast (2019 – 2024). Published Februry. 2019. https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/Real-World-Evidence-Solutions-Market-4954.
- Deloitte Center for Health Solutions. 3rd RWE Benchmarking Study, 2020. Accessed April 27, 2021.
- Berger ML et al. Good practices for real-world data studies of treatment and/or comparative effectiveness: recommendations from the joint ISPOR-ISPE Special Task Force on real-world evidence in health care decision making. Value in Health. 2017;20(8): 1003-1008 https://www.valueinhealthjournal.com/article/S1098-3015(17)33353-3/fulltext.
- Corrigan-Curay J. Framework for FDA’s Real-World Evidence Program. Webinar presented March 15, 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/123160/download. Accessed April 27, 2021.
- Harbeck N, Bartlett M, Spurden D, et al. CDK4/6 inhibitors in HR+/HER2-advanced/metastatic breast cancer: a systematic literature review of real-world evidence studies. Future Oncol. 2021;17(16): 2107-2123. https://www.futuremedicine.com/doi/pdf/10.2217/fon-2020-1264. Accessed July 8, 2021.
- Chen S, Zhou A, Emmanuel B, et al. Systematic literature review of the epidemiology and clinical burden of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Current Medical Research and Opinion. 2020;36(11): 1897-1911. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03007995.2020.1815682.
Accessed July 8, 2021. - Connelley CA, Shirley C, von Kaeppler EP. Cost analyses of prosthetic devices: A systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(7):1404-1415. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33711275/. Accessed July 8, 2021.
Download the PDF version of this solution brief.
Related Resources

Case Study
With as many as 40,000 references per project, Medlior, a HEOR consultancy, used DistillerSR to more accurately and efficiently manage their literature reviews.

Business Brief
Information Overload Drives New Approaches to Managing HEOR Literature Reviews.

Webinar
How Literature Review Automation and Efficient Processes Streamline RWE HEOR Studies


